Introduction
WeGO ups the ante in its treatment of middlewares and entry points. It defines and implements horizontal concerns using a comprehensive set of middlewares. It also lays out guidelines as to what problems must be solved using Middlewares.
WeGO middleware is defined as follows:
type Middleware func(context.Context, *MiddlewareChain) context.Context
A middleware can be defined as a GO function that is called with the intention of invoking a service.The middleware can decide to return back or invoke a downstream chain that in turn passes control to other middlewares. The last middleware in the chain of middlewares actually invokes the service and is hence called service invoker.
In this process, the middleware can enhance the context object and pass it to downstream systems in the chain. It should also return the enhanced version of the middleware back to the caller. The Middleware can also terminate the chain prematurely by returning instead of invoking downstream middlewares.
The Middleware chain is the custodian of the chain of middlewares. It is responsible to invoke the next middleware in a configured chain of middlewares. A middleware chain is set up and the first middleware in the chain is invoked by an entry point. Subsequent middlewares are invoked as the chain progresses.
The WeGO Middlewares & Entry Points
All the middlewares and entry points, service invokers (which itself is the last middleware as explained before) reside in internal/mw package in WeGO. The users can write their own middlewares.
Client Side & Server Side Middlewares
The WeGO middleware interface is identical for both client side and server side middlewares. The passed parameters in the context object are also identical for both client side and server side. This gives a potential for re-use of the same middleware for both client side and server side work. The entire sequence is shown in the diagram below:
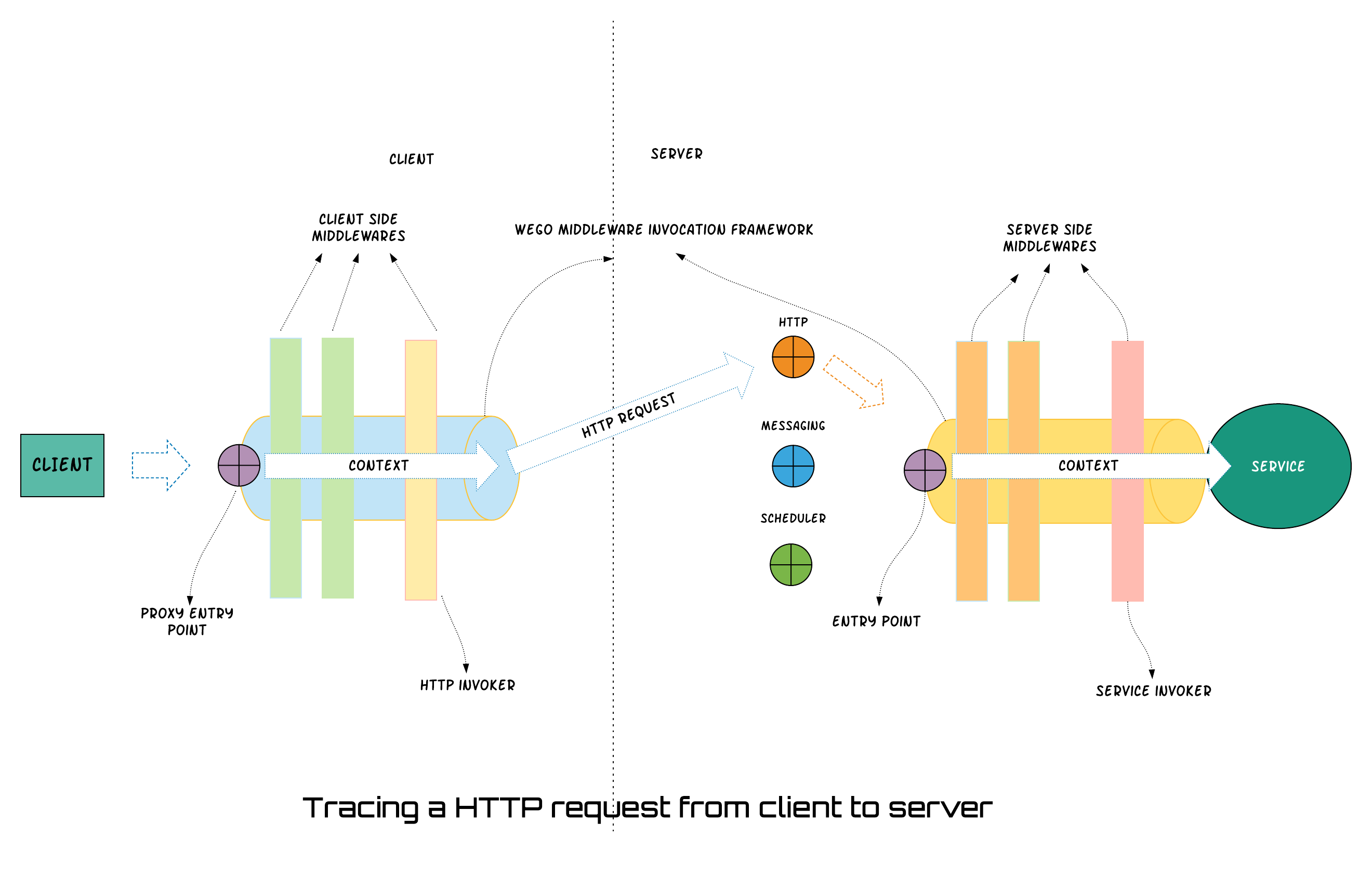
The Entry Points
An entry point is the point of entry to invoke WeGO services or proxies. There are two entry points - one for the server side and the other one for invoking a proxy. The entry point is responsible to set up the other middlewares and start the middleware chain. The entry point then returns the result of the invocation along with any errors encountered.
There are two entry points here. One is the server side entrypoint. Simply called as entry point. The other one is the entry point in client side called proxy entry point.
The Terminators
There are two terminating middlewares in WeGO - one for the client side and the other for the server side. package. These are set up to be the last of the middlewares by the entry points. Terminators will not continue the chain. Instead, they invoke the service either on the client or the server side as discussed below.
The server side entry point sets up service-invoker as the last of the middlewares. Service Invoker’s responsibility is to invoke the actual service with the correct parameters as set up in OperationDescriptor and ParamDescriptor. The arguments are gathered from the context object and are passed to the service. The appropriate method of the service is called with the parameters. Since it internally uses GO reflection, this can panic if the service name or the params are mis-configured. Hence the service invoker resolves this panic and spits out the appropriate error message
The proxy entry point sets up http-invoker as the terminator. This terminator will utilize the information in the ServiceDescriptor to construct the HTTP request. It then uses a configuration property called serviceName + “host_port” to derive the host name for the service. It then issues a request to the hostname. The response is then converted to a GO response. The errors are also appropriately re-created.
Other Middlewares
WeGO supports a flexible middleware strategy which can be introduced at an operation level on both the client and the server side. WeGO also ships with some default middlewares which are discussed below. The responsibilities of WeGO middlewares are as follows:
- Implementing horizontal services such as logging, tracing, auditing, security etc.
- Transformation of the request and response objects.
Middlewares are encouraged to abide by the following principles:
- Avoid writing middlewares which are specific to a particular service.
- Middlewares must access the context object to get and set data.
Following is a description of a few middlewares that ship out of the box with WeGO
Decoder
Decoder decodes the JSON request and converts it into a GOLANG struct of the appropriate type. OperationDescriptor.OpRequestMaker is used to construct the request payload object. JSON parser is used to fill it up from the JSON string. The resulting struct is put as a payload into the context object using:
wegocontext.SetPayload()
The payload then becomes available for other middlewares and terminators. This is the first of the server side middlewares since the payload is needed by other middlewares
V10 Validator
The V10 validator uses v10 to validate the payload. If the payload does not validate correctly, then an error is returned and the chain is discontinued.